Procrastination, is the act of delaying or postponing tasks that require immediate attention. It often emerges when there’s a discrepancy between short-term desires and long-term goals. While it might provide fleeting relief, the consequences of procrastination can be profound . Mindfulness Techniques can be used to manage procrastination
Understanding Procrastination
We’ve all been there, right ? It’s like this little devil on your shoulder saying, “Don’t do that critical task now; you’ve got plenty of time !”, the little voice convinces and takes you to enticing avenues of fun and mental stimulations , and suddenly, you find yourself binge-watching Instagram Reels for hours together or find yourself taking upon itself to complete viewing all the the episodes of the TV series at a go ,or choosing to spring clean your house instead of tackling that looming project.
Procrastination is that insidious force that convinces us to delay important tasks, trade urgency for momentary comfort, and let valuable opportunities slip through our fingers. Yet, the battle against procrastination is not one to be surrendered; it’s a challenge that can be conquered through strategic approaches like Mindfulness Techniques and a deep understanding of its underlying causes.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the complexities of procrastination, unravel its psychological underpinnings, and equip you with a toolbox of effective strategies to triumph over this formidable foe.
Before we delve into the mindfulness techniques that can help combat procrastination, it’s beneficial to gain a deeper understanding of procrastination itself. It’s would be wise to familiarize ourselves with this foe before attempting to overcome it.
“If you know the enemy and know yourself, you need not fear the result of a hundred battles.”
— Sun Tzu
Table of Contents
Scientific reasons behind Procrastination
In the context of procrastination, few researches suggests that some individuals may have differences in their dopamine levels which that can influence their motivation and ability to initiate tasks.
What is Dopamine ?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter and a hormone that plays a crucial role in several functions within the brain and body. It is often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter because of its involvement in feelings of pleasure, reward, motivation, and reinforcement learning.
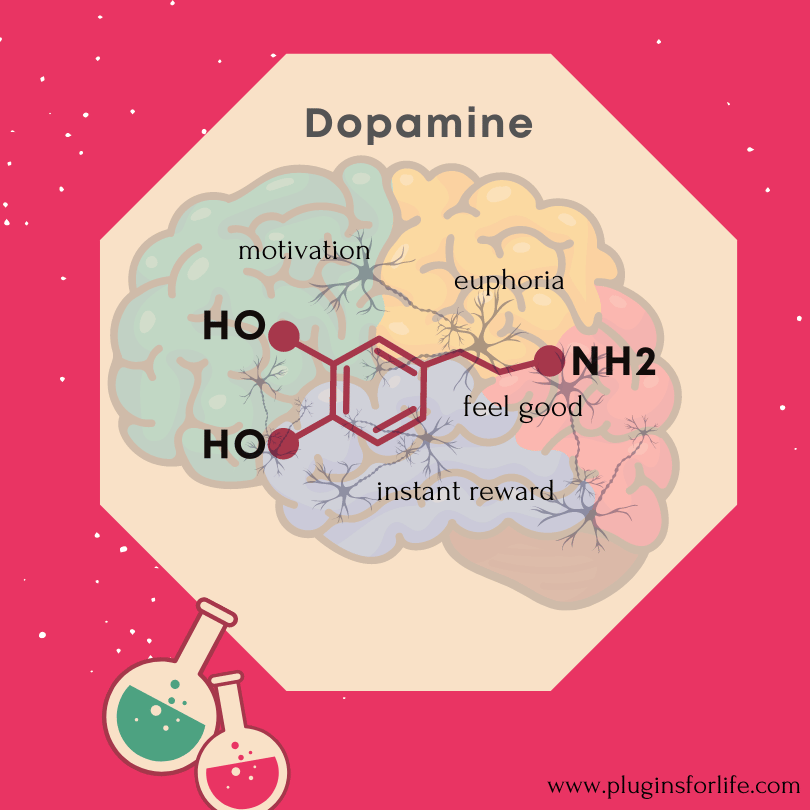
Here are some key functions and roles of dopamine:
- Reward and Pleasure: Dopamine is released when you experience something pleasurable or rewarding. It reinforces behaviors that lead to positive outcomes, encouraging you to repeat those behaviors. This is known as the brain’s reward system.
- Motivation: Dopamine plays a central role in motivation. It helps drive and sustain the motivation needed to pursue goals and tasks. When you achieve a goal or accomplish something, dopamine is released, making you feel motivated and satisfied.
- Emotion Regulation: Dopamine is linked to mood and emotional regulation. Imbalances in dopamine levels have been implicated in conditions like depression and bipolar disorder.
- Cognition and Attention: Dopamine is important for cognitive functions, including attention, memory, and problem-solving. It helps maintain focus and concentration.
In simple terms , dopamine is the chemical in your brain that makes you feel good when you do something enjoyable or rewarding ,so when you put off doing important tasks and instead do things that make you feel good right away, like checking your phone or watching TV. – that Procrastination .
So, dopamine doesn’t directly cause procrastination, but it can make you want to do things that are more immediately satisfying instead of tackling important tasks, which can lead to procrastination.
Other factors which trigger procrastination
One of the main reasons people procrastinate is the tendency to underestimate the time and effort required to complete a task. This leads to a false sense of security, causing individuals to put off important work until the last minute. Procrastination can also be driven by fear of failure or perfectionism, as individuals may delay tasks to avoid potential criticism or disappointment.The desire for perfection can paralyze us, making tasks seem insurmountable. This perfectionist mindset often leads to delay. Lack of Clear Goals is also a strong factor – When goals lack clarity or seem overwhelming, we’re more prone to procrastinate. Ambiguity breeds indecision, which fuels procrastination.
“Procrastination makes easy things hard and hard things harder.”
– Mason Cooley
The Impact of Procrastination on Productivity
Reduced time for important tasks
When you procrastinate, you invariably allocate valuable time to less essential activities or distractions. This leaves lesser time for crucial tasks that contribute directly to your goals and responsibilities. You are basically left to fire-fighting trying to accomplish both quality and quantity in the leftover time , which results in incomplete and substandard output in terms of quality and quantity.
Increased Anxiety , Stress & substandard output
As the deadline approaches , the looming pressure triggers – anxiety and stress , now you realize and feel that you have lesser time which is depleting at a faster rate , and then you enter the panic mode – which leads to avalanches of forced errors , and taking shortcuts to balance the non existent time and ultimately you have a substandard output – both quantity and quality wise – and more than that you would have left yourself exhausted with stress and anxiety .
Missed Opportunities
Procrastination often leads to missed opportunities, whether they’re professional growth prospects, personal achievements, or chances to build valuable connections – professional or personal . Time does not wait , time cannot wait – by delaying action, you can only watch the windows of opportunity close on your face with a thud , limiting your potential for advancement , life enrichment and progress .
Decline in Work Quality:
Rushed and last-minute efforts resulting from procrastination seldom produce work of expected standards of quality. Tasks completed under pressure are more likely to contain forced and unforced errors, will lack creativity, and fail to meet the standards you’re capable of achieving. The rough and wet patches will show through, how much ever you want to hide them . More than that , more than anyone , it would be you who will internally suffer – because deep down you will know – you could have done much better !!
Excellence, nurtured by time, blossoms into a masterpiece.”
– Joydeep Majumder
Damage to Reputation:
Procrastination leading to delivery of substandard and delayed outputs to your clients and stakeholders can erode your reputation over time. Do not forget that reputation is a big marker of decision making of whether a client or a stakeholder would continue his/her association with you or your firm . The decisions they make are based on collective perceptions built over time – judging and compiling your actions, behavior, and track record.
“It takes 20 years to build a reputation and five minutes to ruin it. If you think about that, you’ll do things differently.”
– Warren Buffett
Impaired Decision-Making:
Procrastination often leads to decision fatigue—a state in which your cognitive resources are depleted due to making multiple decisions. As a result, your ability to make well-thought-out decisions diminishes, potentially leading to poor choices.
Lets take an Example :
Imagine you’re an intern at a startup firm – made responsible to create and deliver a logo to a client – the delivery date is fast approaching. You’ve been putting off working on the project for weeks, opting for short-term pleasures like playing table tennis at the office and hanging out with friends. As the delivery date draws closer, you realize you can’t delay any longer and finally sit down to do the preliminary research .
However, because you’ve procrastinated, you’re now faced with a mountain of research material to cover in a limited amount of time.
- You realize that the meeting with client to understand his needs is still not done .
- The client has chosen to go on a vacation and will come back only 4 days before date of delivery – which is a short time
- Your support resource has resigned – and you need to take up that task too.
- Your sibling is not keeping well and you have to make trips to the medical center quite often
The stress of impending delivery date and all that unplanned events combined with the need to make a multitude of decisions about your product delivery strategy contributes to decision fatigue. Your mental energy becomes depleted as you grapple with multiple issues , and you might find yourself making hasty decisions or struggling to prioritize effectively.

In this scenario, procrastination has led to decision fatigue.
In essence, procrastination drains your productivity by redirecting your time and energy away from important tasks. Recognizing the far-reaching effects of procrastination is the first step toward adopting strategies that combat this habit and pave the way for enhanced productivity, improved mental well-being, and greater satisfaction in all areas of your life.Common Scenarios Where Procrastination Arises
Summary of Impact of Procrastination

Strategies to Overcome Procrastination with Mindfulness Techniques
- Breaking Tasks into Smaller Steps
- Setting Specific Goals and Deadlines
- Using the Pomodoro Technique for Focus
- Visualizing the End Result with Mindfulness Techniques
- Practicing the 2-Minute Rule
- Implementing the “Two-Minute Start”
- Cultivating Self-Discipline and Willpower
- Practicing Mindfulness and Self-Awareness
- Developing a Proactive Mindset
- Celebrating Small Wins and Progress
- Transforming Strategies into Habits
- Maintaining Consistency and Momentum
- Tracking Progress and Adjusting Strategies
The Psychology Behind Procrastination
- Instant Gratification Bias: Humans are wired to seek immediate rewards, even if they come at the expense of long-term benefits. This bias leads us to favor easy, enjoyable tasks over important but challenging ones.
- Fear of Failure: Procrastination can serve as a defense mechanism against potential failure. By delaying action, we avoid confronting the possibility of not meeting our own or others’ expectations.
- Lack of Clear Goals: When goals lack clarity or seem overwhelming, we’re more prone to procrastinate. Ambiguity breeds indecision, which fuels procrastination.
- Perfectionism: The desire for perfection can paralyze us, making tasks seem insurmountable. This perfectionist mindset often leads to delay.
Strategies to Conquer Procrastination with Mindfulness Techniques
- Break Tasks into Smaller Steps:The sheer magnitude of a task can trigger avoidance. Break it down into smaller, manageable steps. For example, if you’re avoiding writing a report, start by outlining key sections.
- Set Specific Goals and Deadlines:Vague goals and open-ended timelines invite procrastination. Make your goals precise and assign realistic deadlines. For instance, set a goal to complete a project draft by the end of the week.
- Use the Pomodoro Technique:The Pomodoro Technique involves working in focused intervals (e.g., 25 minutes) followed by a short break. This structure combats the urge to procrastinate by breaking tasks into digestible chunks.
- Visualize the End Result:Create a vivid mental image of the benefits and satisfaction that completing a task will bring. This visualization can counterbalance the allure of procrastination.
- Practice the 2-Minute Rule:If a task can be completed in two minutes or less, do it immediately. This prevents small tasks from accumulating and causing decision fatigue.
- Implement the “Two-Minute Start”:Often, the most challenging part of a task is getting started. Commit to working on a task for just two minutes. Once you begin, momentum often carries you forward.
Conquer Procrastination , using Mindfulness techniques

Procrastination is a universal challenge, but it’s not an insurmountable one. Armed with a profound understanding of its psychological roots and a toolkit of proven strategies, you can overcome the allure of postponement and seize control of your productivity. Remember that progress is a journey, and conquering procrastination is a skill that requires practice and patience. As you incorporate these strategies into your daily life, you’ll find that the once daunting mountain of tasks becomes a series of manageable hills waiting to be conquered. Embrace the battle against procrastination as an opportunity for growth, transformation, and the fulfillment of your long-term goals. The journey begins now—let’s reclaim productivity, one proactive step at a time.
How can I stop procrastinating?
1.Set clear and specific goals.
2.Break tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
3.Prioritize tasks based on importance and deadlines.
4.Create a structured daily or weekly schedule.
5.Use productivity techniques like the Pomodoro Technique
6.Minimize distractions
7.Set a timer to limit the time spent on a task.
8.Use positive reinforcement and rewards for completing tasks.
9.Practice mindfulness and stay present while working.
10.Challenge negative thoughts and perfectionism.
11.Develop self-discipline and build good habits.
12.Find an accountability partner or join a study/group.
13.Eliminate or delegate tasks that are not essential.
14.Seek professional help if procrastination is chronic
Is procrastination and being lazy the same?
Procrastination is the act of delaying or postponing tasks or actions, especially those that are necessary or important. Procrastinators often avoid tasks out of fear, anxiety, or a desire for immediate gratification. It’s more about a struggle with self-regulation, time management, and task avoidance than being inherently lazy.
Laziness, on the other hand, is a tendency to avoid work, effort, or physical activity in general. It often involves a lack of motivation or a desire to do as little as possible. Laziness can manifest as a general aversion to work and responsibility, regardless of the specific task or its importance.
While procrastinators may delay tasks, it doesn’t necessarily mean they are lazy. Procrastination can be a result of various factors, such as perfectionism, lack of confidence, or feeling overwhelmed. In fact, some procrastinators are quite capable and hardworking but struggle with initiating tasks.
Certainly, here’s a bullet list of strategies to help you stop procrastinating:
Set clear and specific goals.
Break tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
Prioritize tasks based on importance and deadlines.
Create a structured daily or weekly schedule.
Use productivity techniques like the Pomodoro Technique (work in focused intervals).
Minimize distractions (e.g., turn off notifications).
Set a timer to limit the time spent on a task.
Use positive reinforcement and rewards for completing tasks.
Practice mindfulness and stay present while working.
Challenge negative thoughts and perfectionism.
Develop self-discipline and build good habits.
Find an accountability partner or join a study/group.
Eliminate or delegate tasks that are not essential.
Seek professional help if procrastination is chronic and affecting your life significantly.
Remember that overcoming procrastination is a gradual process, and it may require experimentation to find the strategies that work best for you.
Is procrastination good or bad?
Positive Aspects of Procrastination:
Creativity and Insight: Some people find that they come up with their best ideas or insights when they procrastinate. Allowing your mind to wander can lead to creative solutions and fresh perspectives.
Stress Reduction: In some cases, taking a break or delaying a task can reduce stress and prevent burnout. It can give you time to recharge and approach the task with a clearer mind.
Negative Aspects of Procrastination:
Missed Deadlines: Procrastination often leads to missed deadlines, which can have negative consequences in academic, professional, and personal settings.
Increased Stress: While brief breaks can reduce stress, chronic procrastination can lead to increased stress and anxiety as deadlines approach.
Reduced Productivity: Procrastination can decrease overall productivity as tasks are postponed and accumulate.
Quality Issues: Rushing to complete a task at the last minute can lead to lower-quality work.
Regret and Guilt: Procrastinators often feel guilty and regretful about not using their time more wisely.
Are procrastinators successful?
Procrastinators can be successful, but chronic procrastination often hinders success. Effective time management and overcoming procrastination are key to achieving success.
Who is most likely to procrastinate?
Certain factors make individuals more likely to procrastinate:
1.Poor time management skills.
2.Perfectionism.
3.Low self-regulation.
4.Low self-efficacy.
5.Task aversion.
6.Lack of motivation.
7.Anxiety and fear of failure.
8.Environmental distractions.
9.Task difficulty.
10.Impaired executive function (e.g., ADHD).
